26807-65-8
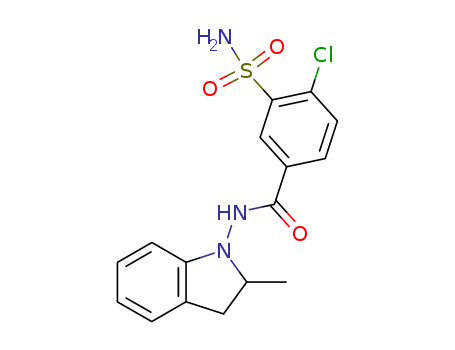
- Product Name:Indapamide
- Molecular Formula:C16H16ClN3O3S
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:365.84
Product Details:
CasNo: 26807-65-8
Molecular Formula: C16H16ClN3O3S
Appearance: Crystalline solid
Wholesale! Buy High Grade Indapamide 26807-65-8 Safe Delivery
- Molecular Formula:C16H16ClN3O3S
- Molecular Weight:365.84
- Appearance/Colour:Crystalline solid
- Melting Point:160-162 °C
- Refractive Index:1.693
- Boiling Point:110.4°C (rough estimate)
- PKA:pKa (25°) 8.8 ± 0.2
- PSA:100.88000
- Density:1.51 g/cm3
- LogP:4.32040
Indapamide(Cas 26807-65-8) Usage
| Category | Indapamide is classified as a thiazide-like diuretic, commonly referred to as a "water pill." It is primarily used in the management of hypertension (high blood pressure) and fluid retention associated with congestive heart failure. |
| Definition | Indapamide is a diuretic that increases urine output, aiding in the removal of excess fluid from the body. |
| Properties | Solubility: Moderately soluble in water Pharmacokinetics: Indapamide is well-absorbed orally, with its peak plasma concentration reached within 1-2 hours for immediate-release and 8-12 hours for sustained-release formulations. |
| Uses | High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Indapamide is commonly prescribed, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, to manage high blood pressure. By reducing the volume of circulating fluid in the body, it decreases the workload on the heart and blood vessels, thereby lowering blood pressure. Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): It helps treat edema (fluid retention) caused by congestive heart failure. By promoting the excretion of sodium and water, indapamide reduces swelling and alleviates symptoms such as shortness of breath. |
| Side Effects | Common Side Effects: Fatigue, dizziness, headache, muscle cramps, and dehydration. Serious Side Effects: Hypokalemia (low potassium), hyponatremia (low sodium), hypotension (low blood pressure), arrhythmias, and kidney dysfunction. Severe Hypokalemia: Although rare, it can be a serious risk, particularly in the initial months of therapy. Monitoring electrolyte levels helps mitigate this risk, especially when using sustained-release formulations. |
| Clinical Insights | In large population-based studies, indapamide has shown low risk of severe side effects (such as hypokalemia) with sustained-release formulations. When combined with perindopril, indapamide has demonstrated significant cardiovascular benefits, including reductions in all-cause mortality, cardiovascular death, and stroke, making it a key option for managing high-risk hypertension. |
InChI:InChI=1/C16H16ClN3O3S/c1-10-8-11-4-2-3-5-14(11)20(10)19-16(21)12-6-7-13(17)15(9-12)24(18,22)23/h2-7,9-10H,8H2,1H3,(H,19,21)(H2,18,22,23)
26807-65-8 Relevant articles
Incidence of severe hypokalaemia in patients taking indapamide
IM - ORIGINAL
, Internal and Emergency Medicine, Volume 18, pages 549–557, (2023)
In this large population-based study with 147,319 person-years of follow-up, severe hypokalaemia requiring hospitalisation was uncommon among hypertensive patients on indapamide. The risk is higher in women and in the initial weeks and months after starting therapy. The use of the sustained-release formulation reduces the risk. We conclude that using indapamide to treat hypertension is safe, even in the elderly, especially if the sustained-release formulation is used and electrolytes are monitored periodically.
Pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology of indapamide
Frank S Caruso Ph.D., Romana R Szabadi Ph.D., Robert A Vukovich Ph.D.
American Heart Journal Volume 106, Issue 1, Part 2, July 1983, Pages 212-220
Disappearance of indapamide from the blood is biphasic, with a terminal half-life of approximately 16 hours. Renal clearance represents less than 10% of the total systemic clearance of the parent drug, showing the dominant role of hepatic clearance. Studies of 14C-labeled indapamide in humans demonstrate that 70% of the radioactivity is excreted in urine and 23% in feces.
26807-65-8 Process route
-
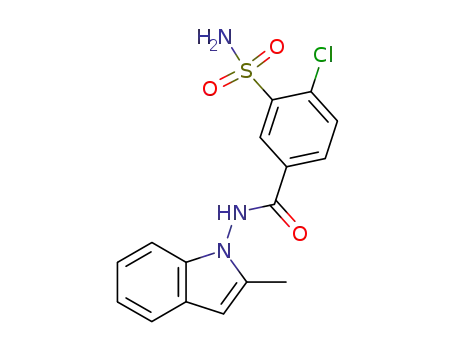
- 63968-75-2
Dehydroindapamide

-
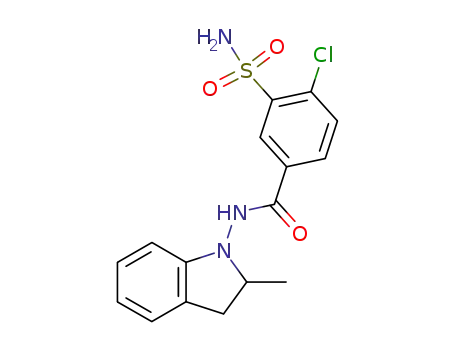
- 26807-65-8,77083-52-4
Indapamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium tetrahydroborate; hexachloroplatinic acid; hydrogen; In ethanol; at 10 ℃; for 1h;
|
99.3% |
-
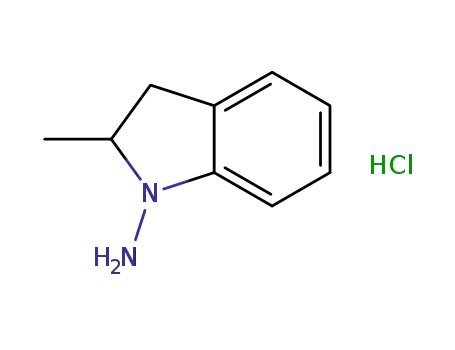
-
N-amino-2-methylindoline hydrochloride
-
-
C8H5Cl2NO5S

-

- 26807-65-8,77083-52-4
Indapamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With triethylamine; In dichloromethane; at 15 ℃; for 6h; Temperature; Solvent;
|
96.89% |
26807-65-8 Upstream products
-
1205-30-7
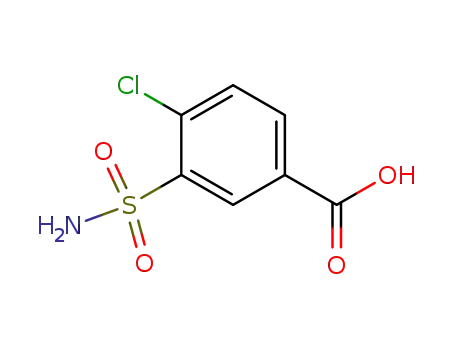
4-chloro-3-sulphamoylbenzoic acid
-
31529-46-1
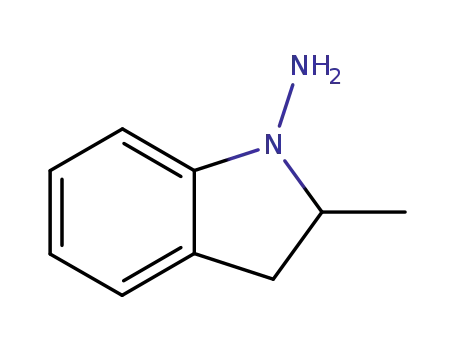
1-amino-2,3-dihydro-2-methylindole
-
70049-77-3
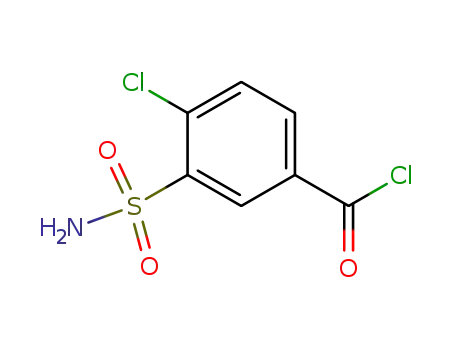
3-(aminosulfonyl)-4-chlorobenzoyl chloride
-
7440-44-0
pyrographite
26807-65-8 Downstream products
-
63968-75-2

Dehydroindapamide
-
77083-52-4
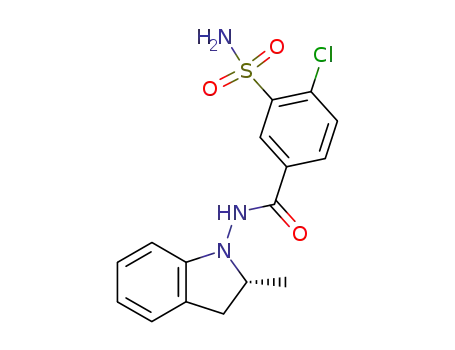
(R)-indapamide
-
77083-52-4
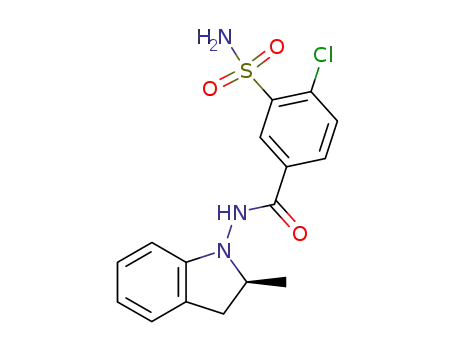
(S)-indapamide
-
1108610-87-2
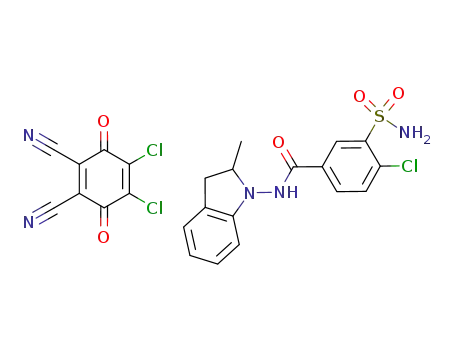
C8Cl2N2O2*C16H16ClN3O3S
Relevant Products
-
Tirofiban Hcl
CAS:142373-60-2
-
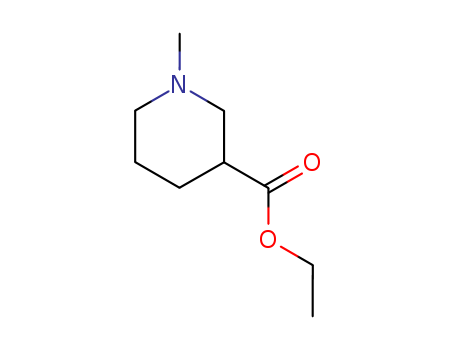
Ethyl 1-methylpiperidine-3-carboxylate
CAS:5166-67-6
-
Lasmiditan Hemisuccinate
CAS:439239-92-6